How To Calculate CPF Contribution
Find out how CPF contributions are computed and the legal requirements.

What is CPF?
The CPF is a mandatory savings scheme funded by contributions from both employers and employees. It ensures that individuals have a secure financial future by providing for retirement, medical, and housing needs.
Employer and Employee Contributions
Employers are required to make monthly CPF contributions for their Singaporean and PR employees who earn more than $50 per month. Their contributions are deducted from their wages and combined with the employer’s contribution before being credited to their CPF accounts.
CPF Contribution Rates for Singaporeans
CPF contribution rates vary based on the employee’s age and wage band. For employees under 55, the contribution rate is typically 37% of their monthly wage, with 17% coming from the employer and 20% from the employee.
Here’s a look at the present contribution rates (as of 01 June 2024):
| Employee’s Age (Years) | Total (% of wage) | By employer (% of wage) | By employee (% of wage) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 55 and below | 37 | 17 | 20 |
| Above 55 to 60 | 31 | 15 | 16 |
| Above 60 to 65 | 22 | 11.5 | 10.5 |
| Above 65 to 70 | 16.5 | 9 | 7.5 |
| Above 70 | 12.5 | 7.5 | 5 |
CPF Allocations
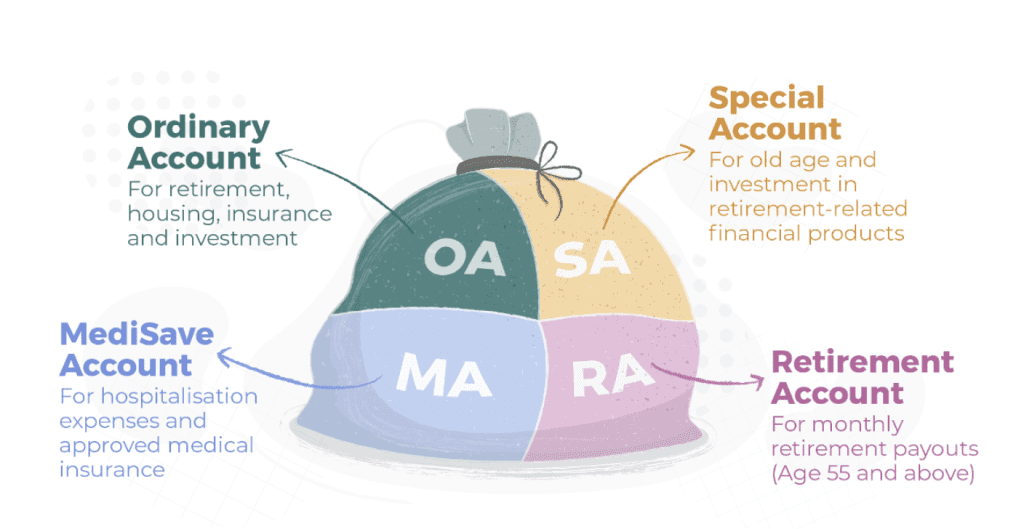
Monthly CPF contribution will be further allocated to various accounts. Each CPF contributor starts off with three accounts:
Ordinary Account (OA):
- Used for housing, insurance, investment, and education.
Special Account (SA):
- Intended for old age and investment in retirement-related financial products.
MediSave Account (MA):
- Used for hospitalisation expenses and approved medical insurance.
Retirement Account (RA):
- Upon turning 55, there’ll be a fourth account, the Retirement Account (RA).
Who is Considered an Employee?
Under the CPF Act, an employee is defined as:
- A person who is employed in Singapore under a Contract of Service (COS); or
- A Singapore Citizen who is employed under a contract of service or other agreement entered into in Singapore as a master, seaman, or apprentice in any vessel.
If you’re a Singapore Citizen or Permanent Resident employee earning total wages of more than $50 per month, your employer must contribute CPF for you. An employee can be employed on a full-time, part-time, temporary, contract, or casual basis.
Employer Obligations
- Timely Contributions:
- Employers must pay CPF contributions by the 14th of each month. Late payments incur interest charges and potential penalties.
- Submission of CPF Details:
- Use the CPF e-Submit@web service to declare and pay CPF contributions online. Ensure accurate reporting of employees’ wages and CPF contributions.
- Maintaining Records:
- Keep detailed records of wage payments and CPF contributions for all employees for at least one year.
- Additional Contributions:
- Beyond mandatory contributions, employers can make voluntary top-ups to employees’ CPF accounts as a form of additional benefit.
CPF Compliance and Penalties
Non-compliance with CPF regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment. Therefore, it’s imperative to set a fixed routine for monthly payroll and regularly check for updates on CPF policies from the CPF Board’s official website.
CPF for Permanent Residents and Additional Levies
It’s worth noting that CPF contribution rates differ for employees who are non-Singapore citizens or permanent residents.
Understanding the exact contributions for PRs, alongside other statutory requirements such as the Skills Development Levy (SDL), Chinese Development Assistance Council (CDAC) Fund, and Self-Help Groups (SHG) contributions, can be complex.
Employers and employees are advised to refer to the CPF Board’s website or consult a qualified professional for more detailed information.
To simplify these calculations, you can use SBO’s Free CPF Calculator. This tool helps you calculate both your CPF contributions and statutory donations accurately, ensuring compliance and ease of financial planning.
Explore More Content
Table of Content

